Homeopathy Origin: Historical Background of Homeopathy
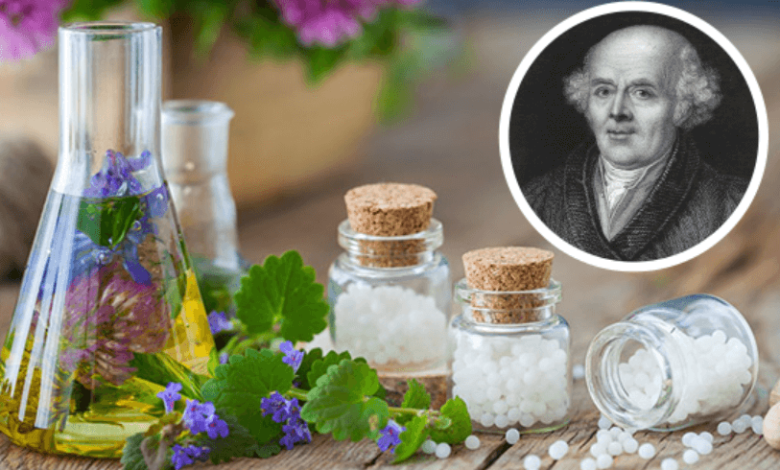

The origins of homeopathy can be traced back to the late 18th century, a period marked by a growing disillusionment with traditional medical practices. Samuel Hahnemann, a German physician, emerged as a pivotal figure in this transition, advocating for a system that prioritized individualized treatment through the use of highly diluted substances. His foundational text, “Organon of Medicine,” introduced principles that would challenge prevailing medical paradigms. However, the complexities surrounding homeopathy’s evolution and its acceptance in contemporary medicine raise intriguing questions about its ongoing relevance and the scientific scrutiny it faces. What factors have influenced its journey?
Early Medical Practices
In the context of ancient civilizations, early medical practices laid the groundwork for various healing traditions, including homeopathy.
Ancient remedies, derived from a rich tapestry of herbal traditions, showcased the profound understanding of nature’s therapeutic potential.
These practices emphasized holistic healing and the balance of bodily elements, influencing subsequent medicinal approaches and contributing to the evolution of health care systems that prioritize natural and individualized treatments.
Samuel Hahnemann’s Contributions
Samuel Hahnemann’s pioneering work in the late 18th and early 19th centuries fundamentally reshaped the landscape of medical practice through the establishment of homeopathy.
Hahnemann’s experiments on drug effects and his systematic observations laid the groundwork for homeopathic principles. His writings, particularly the “Organon of Medicine,” articulated a coherent framework that challenged conventional practices, advocating for individualized patient care and the use of highly diluted remedies.
Also read: Homeopathy Medicines: List of Medicines Used in Homeopathy
Principles of Homeopathy
Homeopathy operates on several core principles that distinguish it from conventional medicine, with three foundational concepts being particularly noteworthy: the Law of Similars, the Law of Infinitesimals, and the principle of individualized treatment.
Remedy selection relies on matching symptoms with specific homeopathic remedies, while potentization methods enhance the efficacy of these remedies, ensuring a tailored approach that respects each individual’s unique health needs.
Evolution and Acceptance
The development of homeopathy can be traced through a complex interplay of philosophical, scientific, and cultural influences since its inception in the late 18th century.
Over time, public perception has shifted, with increased homeopathy adoption reflecting a growing desire for alternative therapies.
This evolution highlights the ongoing debate between conventional medicine and homeopathic practices, illustrating the dynamic nature of healthcare preferences in contemporary society.
Also read: Homeopathy Medicine: Overview of Homeopathic Medical Treatments
Conclusion
In summation, the origins of homeopathy reveal a complex tapestry woven from historical medical practices and innovative ideas introduced by Samuel Hahnemann. Through the delicate interplay of individualized care and the principles of potentization, homeopathy emerged as a distinct approach to healing, challenging conventional paradigms. This evolution, marked by both skepticism and acceptance, continues to resonate in contemporary discussions about holistic health practices, symbolizing a persistent quest for balance between tradition and modernity within the realm of medicine.